Tight Junctions in Cancer Metastasis: Unveiling the Gatekeepers of Tumor Progression

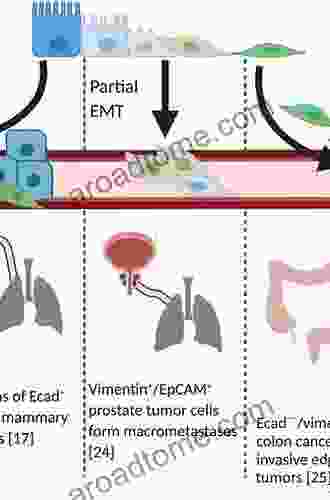
Cancer metastasis, the spread of malignant cells from their primary site to distant organs, is a major cause of cancer-related deaths. Metastasis is a complex process involving multiple steps, including the disruption of cell-cell adhesion, invasion through the extracellular matrix, intravasation into the bloodstream, survival in the circulation, extravasation into the target organ, and colonization at the secondary site. Tight junctions (TJs),intercellular junctions that regulate cell polarity, permeability, and adhesion, play a crucial role in the metastatic cascade.
Tight junctions are multi-protein complexes that form the apical most junction between adjacent epithelial and endothelial cells. They are composed of three main protein families: claudins, occludins, and junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs). Claudins and occludins are transmembrane proteins that interact in a homophilic and heterophilic manner to form the backbone of the TJ, while JAMs are single-pass transmembrane proteins that contribute to TJ assembly and function. TJs regulate paracellular permeability by controlling the passage of ions, solutes, and macromolecules through the intercellular space. They also play a role in cell-cell adhesion, cell polarity, and the maintenance of tissue architecture.
Alterations in TJ structure and function are commonly observed in cancer cells, and these changes are associated with increased metastatic potential. Loss of TJ proteins, such as claudins and occludins, has been linked to a decrease in cell-cell adhesion, increased paracellular permeability, and enhanced cell migration and invasion. Conversely, overexpression of certain TJ proteins, such as claudin-4, has been associated with increased tumor growth and metastasis.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6120 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 567 pages |
The mechanisms underlying TJ disruption in cancer are complex and involve multiple factors, including genetic mutations, epigenetic modifications, and alterations in signaling pathways. Mutations in TJ genes, such as claudin-1, -4, and -7, have been identified in various types of cancer, including breast, lung, and colorectal cancer. These mutations can lead to loss of TJ function, increased paracellular permeability, and enhanced metastatic potential.
Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone deacetylation, can also contribute to TJ disruption in cancer. Aberrant DNA methylation of TJ gene promoters has been associated with decreased expression of TJ proteins and increased cancer cell migration and invasion. Histone deacetylation can also lead to TJ disruption by altering the expression of TJ-associated genes.
Alterations in signaling pathways, such as the Wnt/β-catenin and TGF-β pathways, can also affect TJ function in cancer. Activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway has been linked to increased expression of claudins, which can promote cancer cell migration and invasion. Conversely, inhibition of the TGF-β pathway has been shown to decrease claudin expression and reduce cancer cell motility.
The role of TJs in cancer metastasis provides potential therapeutic opportunities. Targeting TJs could inhibit tumor progression and metastasis by restoring cell-cell adhesion, reducing paracellular permeability, and blocking cell migration and invasion. Several strategies are being explored to target TJs for cancer therapy, including:
- Inhibitors of TJ proteins: Small molecule inhibitors and antibodies targeting TJ proteins, such as claudins and occludins, are being developed to disrupt TJ function and inhibit cancer cell migration and invasion.
- Modulators of TJ signaling pathways: Drugs that modulate TJ-associated signaling pathways, such as the Wnt/β-catenin and TGF-β pathways, could restore TJ function and inhibit cancer metastasis.
- Exploiting TJ-specific biomarkers: Identifying TJ-specific biomarkers could help predict metastatic potential and guide therapeutic decisions.
Tight junctions play a critical role in cancer metastasis by regulating cell-cell adhesion, permeability, and polarity. Alterations in TJ structure and function are commonly observed in cancer cells and are associated with increased metastatic potential. Targeting TJs could provide novel therapeutic strategies for inhibiting cancer progression and metastasis.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6120 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 567 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia T J Waters
T J Waters Richard Carlson
Richard Carlson Tatyana Fagerjord
Tatyana Fagerjord Shlomo Aloni
Shlomo Aloni William S Turley
William S Turley Yue Zhang
Yue Zhang Yvonne Perkins
Yvonne Perkins Stephanie Nauli
Stephanie Nauli William Butler
William Butler Sibahle Zulu
Sibahle Zulu Todd Finnerty
Todd Finnerty Summer Greene
Summer Greene Sarah E Truman
Sarah E Truman Sandy Antunes
Sandy Antunes James Rallison
James Rallison Tiffany Kuhn
Tiffany Kuhn Tony Allen Gaskins Jr
Tony Allen Gaskins Jr Scott Walbridge
Scott Walbridge Christopher Kenworthy
Christopher Kenworthy Susan Harvard
Susan Harvard
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Chris ColemanIntroducing The New Sonoma Diet Plan: A Revolutionary Approach to Sustainable...
Chris ColemanIntroducing The New Sonoma Diet Plan: A Revolutionary Approach to Sustainable... Douglas PowellFollow ·8k
Douglas PowellFollow ·8k Ryan FosterFollow ·11.7k
Ryan FosterFollow ·11.7k Yasunari KawabataFollow ·3.1k
Yasunari KawabataFollow ·3.1k Carson BlairFollow ·5.5k
Carson BlairFollow ·5.5k Alfred RossFollow ·18.9k
Alfred RossFollow ·18.9k Dashawn HayesFollow ·7.3k
Dashawn HayesFollow ·7.3k Charles BukowskiFollow ·4.8k
Charles BukowskiFollow ·4.8k D'Angelo CarterFollow ·7.1k
D'Angelo CarterFollow ·7.1k

 Timothy Ward
Timothy WardSteamy Reverse Harem with MFM Threesome: Our Fae Queen
By [Author...

 Cody Blair
Cody BlairThe Ultimate Guide to Energetic Materials: Detonation and...
Energetic materials are a fascinating and...

 Kenzaburō Ōe
Kenzaburō ŌeProstitution, Modernity, and the Making of the Cuban...
By Emily A....

 Kirk Hayes
Kirk HayesUnveil the Enchanting World of The Rape of the Lock by...
Alexander Pope's epic...

 Ivan Turgenev
Ivan TurgenevTantric Quest: An Encounter With Absolute Love
Embark on a Tantric Quest to...

 Gary Reed
Gary ReedThe Darwin Awards: Evolution in Action
The Darwin Awards are a...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6120 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 567 pages |